What is Kubernetes Gateway API
Kubernetes Gateway API (hereinafter referred to as KGA) was proposed by the sig-network group as a collection of resources to help users model service networks in K8S.
It helps users plan the service network within the cluster by providing standardized interfaces that allow various vendors to provide their own implementations.
Evolution History
Initially, K8S provided the Ingress API to allow users to define the entrance network of the cluster. With the increase in traffic management requirements (circuit breaking, rate limiting, canary release), the initial definition of Ingress could no longer meet the needs, so the community began to split into different implementations.
- Extend
IngressusingCRD, for example: https://dave.cheney.net/paste/ingress-is-dead-long-live-ingressroute.pdf - Extend
IngressusingAnnotation, for example: nginx-controller
Although these methods can solve existing problems, they also led to:
- No unified standard, each ingress-controller implements it in its own way.
- No portability.
Therefore, KGA came into being. KGA needs to allow users to easily use the following functions:
Traffic Management
- HTTP traffic can be routed by
Header,URI. - Traffic routing by weight.
- Traffic mirroring.
- TCP and UDP routing, etc.
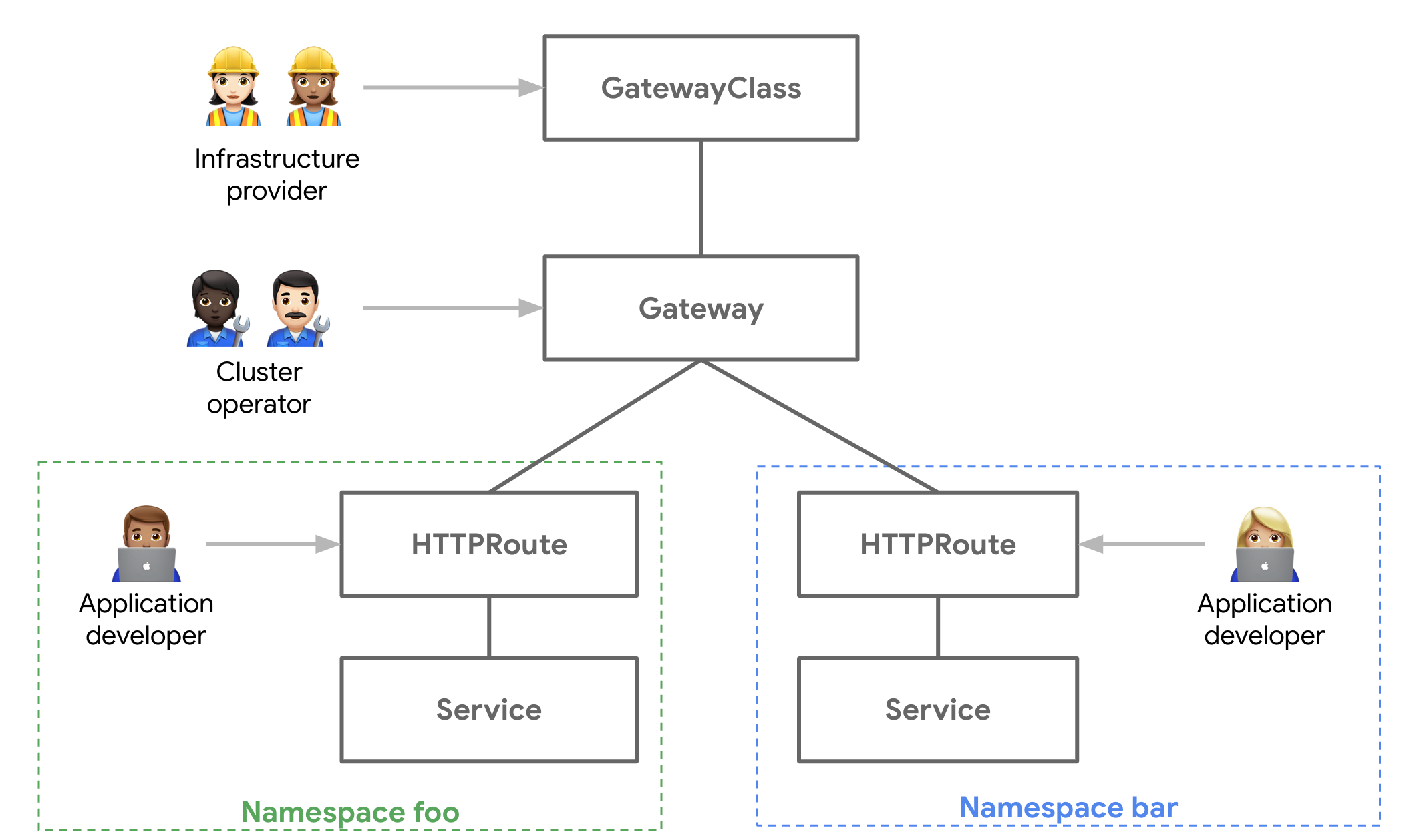
Role-Oriented Design
- Separate the roles of Routing and Service.
Extensibility
- Supports hierarchical configuration, users can add or override attributes in lower-level configurations in upper-level configurations.
Flexible Consistency
- KGA provides three levels of API
- core
- Must be implemented.
- extended
- Can be unimplemented, if implemented, portability must be guaranteed.
- custom
- Each controller can customize, and no portability guarantee is required.
KGA
To meet the above functions, KGA provides the following APIs:
- GatewayClass
Specifies the implementation of KGA (such as istio or nginx), similar to StorageClassess.
- Gateway
Specifies which GatewayClass the Route should use.
- Route
Defines specific routing rules, such as HTTPRoute, TCPRoute, UDPRoute.
Specifies which Service the traffic matching the rules should be routed to.
For specific fields of each API, you can view this document
Example
There are the following common scenarios:
The foo team needs to deploy multiple services in the foo namespace and requires http requests to be routed to different Services according to uri.
kind: HTTPRoute
apiVersion: networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: foo-route
namespace: foo
labels:
gateway: external-https-prod
spec:
hostnames:
- "foo.example.com"
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: Prefix
value: /login
forwardTo:
- serviceName: foo-auth
port: 8080
- matches:
- path:
type: Prefix
value: /home
forwardTo:
- serviceName: foo-home
port: 8080
- matches:
- path:
type: Prefix
value: /
forwardTo:
- serviceName: foo-404
port: 8080
The bar team deploys services in the bar namespace and needs to canary release their services, sending traffic to bar-v1 and bar-v2 at a ratio of 9:1 respectively, and when the request Header contains env: canary, the traffic is published to bar-v2.

kind: HTTPRoute
apiVersion: networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: bar-route
namespace: bar
labels:
gateway: external-https-prod
spec:
hostnames:
- "bar.example.com"
rules:
- forwardTo:
- serviceName: bar-v1
port: 8080
weight: 90
- serviceName: bar-v2
port: 8080
weight: 10
- matches:
- headers:
values:
env: canary
forwardTo:
- serviceName: bar-v2
port: 8080
When the two teams have created HTTPRoute, how to match the ingress traffic to these rules? Here Gateway is needed.
The infra team can create the following Gateway to bind Routes.
kind: Gateway
apiVersion: networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: prod-web
spec:
gatewayClassName: acme-lb
listeners:
- protocol: HTTPS
port: 443
routes:
kind: HTTPRoute
selector:
matchLabels:
gateway: external-https-prod
namespaces:
from: All
tls:
certificateRef:
name: admin-controlled-cert
You can see that the Gateway uses selector.matchLabels to select HTTPRoute with gateway: external-https-prod Label under all namespaces.
At the same time, the Gateway specifies gatewayClassName as acme-lb, so these route rules will be synchronized to acme-lb.
Therefore, as long as the dns of foo.example.com and bar.example.com are resolved to the externalIP of acme-lb, traffic routing can be completed.
The following is the topology diagram of these APIs
